Multi-Cloud Security: Proven Methods for Safeguarding Data

Ofir Stein
July 8, 2024

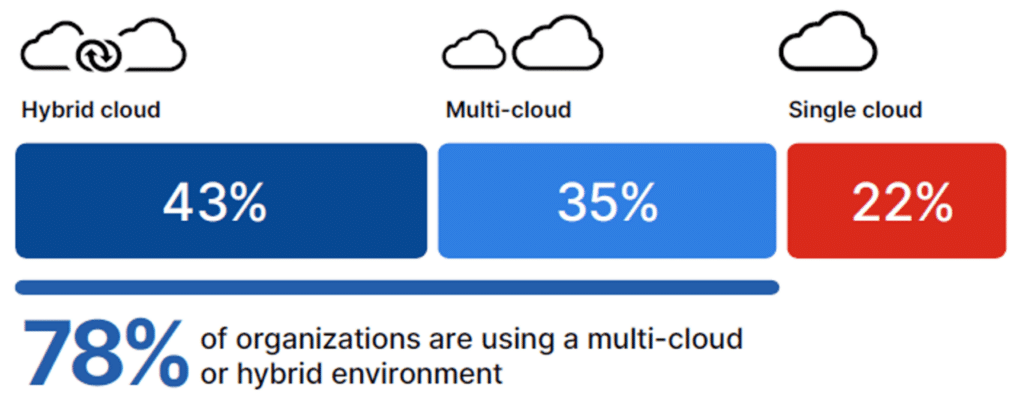
As organizations increasingly adopt diverse cloud services to meet their varying computational and storage needs, multi-cloud security emerges as a critical concern. “In 2024, a majority of organizations (78%) are opting for hybrid and multi-cloud strategies. Of those organizations, 43% use a hybrid of cloud and on-premises infrastructure, and 35% have a multi-cloud strategy,” according to the 2024 Fortinet Cloud Security Report.
This approach not only amplifies the benefits of cloud computing but also introduces complex challenges in safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring robust data governance. Thus, the significance of multi-cloud security cannot be overstated, as it plays a fundamental role in protecting data across multiple cloud environments from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
The Basics of Multi-cloud Security
What is Multi-cloud Security?
Multi-cloud security refers to the protective measures and strategies implemented to safeguard data, applications, and infrastructures when utilizing multiple cloud service providers such as AWS, Azure, and GCP. This approach is crucial in a world where businesses leverage diverse cloud environments to enhance flexibility, resilience, and cost optimization. It addresses the complexities of managing varied cloud resources, ensuring seamless data integration and robust security across all platforms.
Why is It Essential?
The essence of multi-cloud security lies in its ability to provide a unified security posture across various cloud platforms, which is vital for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive data. Organizations face numerous challenges such as cyber threats, unauthorized access, and potential data breaches. Implementing a comprehensive multi-cloud security strategy mitigates these risks, enhances data governance, and supports compliance with data sovereignty requirements.
Multi-cloud Security Key Statistics
Recent studies underscore the importance and rapid adoption of multi-cloud strategies:
- Adoption Rates: 62% of organizations are currently utilizing a multi-cloud environment, with an additional 18% in the transition phase.
- Growth Projection: Approximately 64% of businesses expect their use of multi-cloud to increase over the next two years.
- Security Concerns: About 51% of IT leaders express reluctance in expanding to additional clouds due to the complexities of maintaining security across multiple platforms.
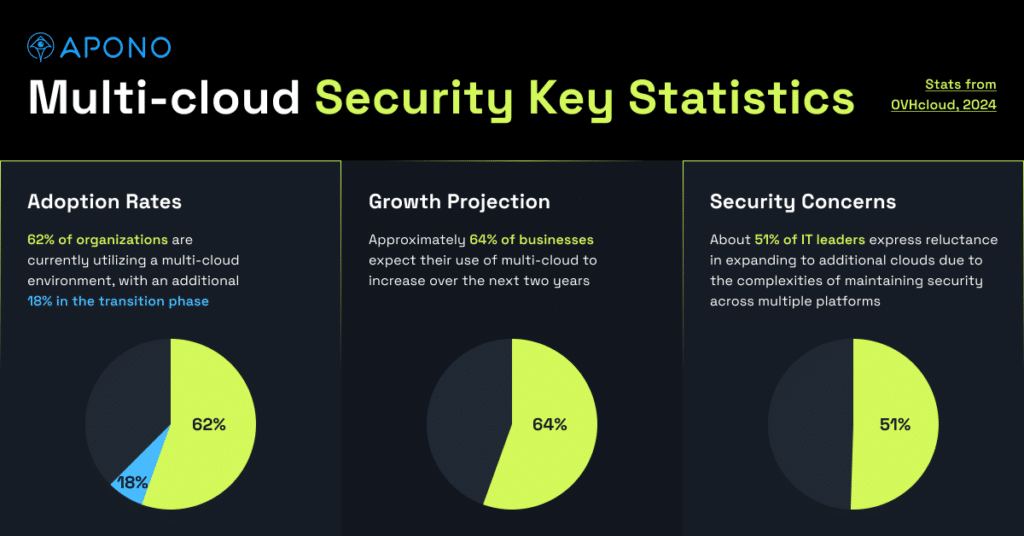
These statistics highlight the growing reliance on multi-cloud environments and the critical need for effective security measures to protect organizational assets and ensure operational continuity.
Top Benefits of Multi-cloud Strategies
Access to Diverse Services
Multi-cloud strategies allow organizations to leverage a wide array of services from various cloud providers, each offering unique capabilities and features. By utilizing multiple clouds, businesses can select the most suited provider for specific tasks, such as one specializing in data storage and security while another excels in big data analytics. This approach not only ensures that organizations can employ the best-of-breed services for their specific needs but also fosters innovation by integrating diverse technologies like Kubernetes, which supports application portability across different environments.
Enhanced System Reliability
One of the most significant advantages of adopting a multi-cloud strategy is the improvement in system reliability and uptime. By distributing workloads across multiple cloud platforms, organizations can minimize the risk of service disruptions. If one cloud platform experiences an outage, the workload can be seamlessly shifted to another provider, ensuring uninterrupted access to resources and services. This redundancy is crucial for maintaining continuous service availability and operational continuity.
Agility and Quick Responses to Changes
Multi-cloud environments provide businesses with the flexibility to quickly adapt to changing market dynamics and technological advancements. The ability to switch between providers or distribute workloads across multiple clouds reduces the risk of vendor lock-in and enhances organizational agility. This strategic flexibility allows companies to respond swiftly to opportunities or challenges, ensuring they remain competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. Additionally, the scalability of cloud resources enables organizations to efficiently manage demand spikes or decreases, optimizing cost and performance.
Key Challenges in Multi-cloud Security
Managing Increased Complexity
One of the primary challenges in multi-cloud security is managing the increased complexity that comes with operating across multiple cloud platforms. Each provider has its own set of tools, interfaces, and security protocols, making it difficult for organizations to maintain a clear oversight of their data and resources. This complexity often leads to challenges in data integration and consistent monitoring, increasing the risk of security gaps and data inconsistencies.
Achieving Consistent Security Policies
Achieving consistent security policies across various cloud environments is another significant challenge. Organizations must ensure that their security measures are uniformly enforced across all platforms to protect sensitive data from threats. However, differences in cloud architectures and service models can complicate the implementation of uniform security policies. Organizations need to develop comprehensive security frameworks that are adaptable to the specific requirements of each cloud provider while maintaining overall security standards.
Mitigating an Expanded Attack Surface
The use of multiple cloud services inherently expands an organization’s attack surface. Each additional service and integration point introduces potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cyber attackers. Ensuring robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security assessments, is crucial to mitigate these risks. Organizations must also stay vigilant against emerging threats and continuously update their security practices to protect their multi-cloud environments.
Implementing Effective Multi-cloud Security Measures
Identity Access Management (IAM)
Effective multi-cloud security begins with robust Identity Access Management (IAM). IAM systems control who accesses cloud resources by enforcing multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and other security measures. This acts like a sophisticated key card system, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access specific resources within the multi-cloud environment. Regular audits of user roles and permissions help maintain this control, preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding sensitive information.
Data Encryption and Secure Transfers
Data encryption is critical for protecting data both in transit and at rest across multiple cloud platforms. Utilizing advanced encryption methods, such as AES 256-bit encryption, ensures that data remains secure, whether it is stored locally or transferred across cloud environments. Moreover, securing data transfers between different cloud platforms is essential and can be achieved through encryption and secure network connections. This layer of security protects data from being intercepted and accessed by unauthorized parties.
Regular Audits and Assessments
Conducting regular security audits and assessments is vital to uncover and address security vulnerabilities across all cloud platforms. These audits should include a comprehensive evaluation of the organization’s security posture, identifying any potential threats and vulnerabilities. By continuously monitoring the multi-cloud system in real time and regularly auditing security measures, organizations can maintain adherence to security policies and regulatory requirements, ensuring ongoing protection against potential cyber threats.
Implementing these measures will significantly enhance the security of multi-cloud environments, enabling organizations to leverage the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing risks.
Conclusion
It’s clear that the journey towards achieving secure multi-cloud environments is ongoing and requires continuous adaptation to emerging threats and evolving cloud technologies. The significance of adopting a strategic, well-rounded approach to multi-cloud security cannot be overstated, as it underpins the integrity and resilience of modern digital infrastructures. With the right mix of strategic planning, technological implementation, and constant vigilance, organizations can harness the full potential of multi-cloud computing, turning the challenges of security into opportunities for fostering innovation, enhancing system reliability, and driving business growth.
How Apono Helps
Apono secures multi-cloud environments by leveraging a robust, scalable architecture that eliminates the need for permanent credentials. It employs ephemeral certificate-based authentication, which ensures that access permissions are granted only when needed and for a limited duration. This approach minimizes the risk of credential theft and unauthorized access. Additionally, Apono facilitates centralized access management across diverse cloud platforms, allowing organizations to enforce consistent security policies. Through its seamless integration with existing identity providers and comprehensive audit trails, Apono enhances visibility and control, enabling organizations to maintain stringent security standards in complex, multi-cloud ecosystems.