How to Prevent Insider Threats: Implementing Least Privilege Access Best Practices

Rom Carmel
November 18, 2024

Organizations lose $16.2 million annually (up from $15.4 million) due to insider threats. Many businesses still can’t prevent these threats effectively. Malicious or negligent employees continue to risk sensitive data and systems despite strong external security measures. Security professionals must solve a big challenge – protecting against insider threats while keeping operations running smoothly.
Understanding the Insider Threat Landscape
Organizations face a rising wave of insider threats. Recent data reveals that 76% of organizations now report insider attacks, up from 66% in 2019. Business and IT complexities make it harder for organizations to handle these risks effectively.
Current Statistics and Trends
In 2023, 60% of organizations reported experiencing an insider threat in the last year. The number of organizations dealing with 11-20 insider attacks grew five times compared to the previous year. Containing these incidents remains challenging. Teams need 86 days on average to contain an insider incident, and only 13% manage to do it within 31 days.
Impact on Business Operations
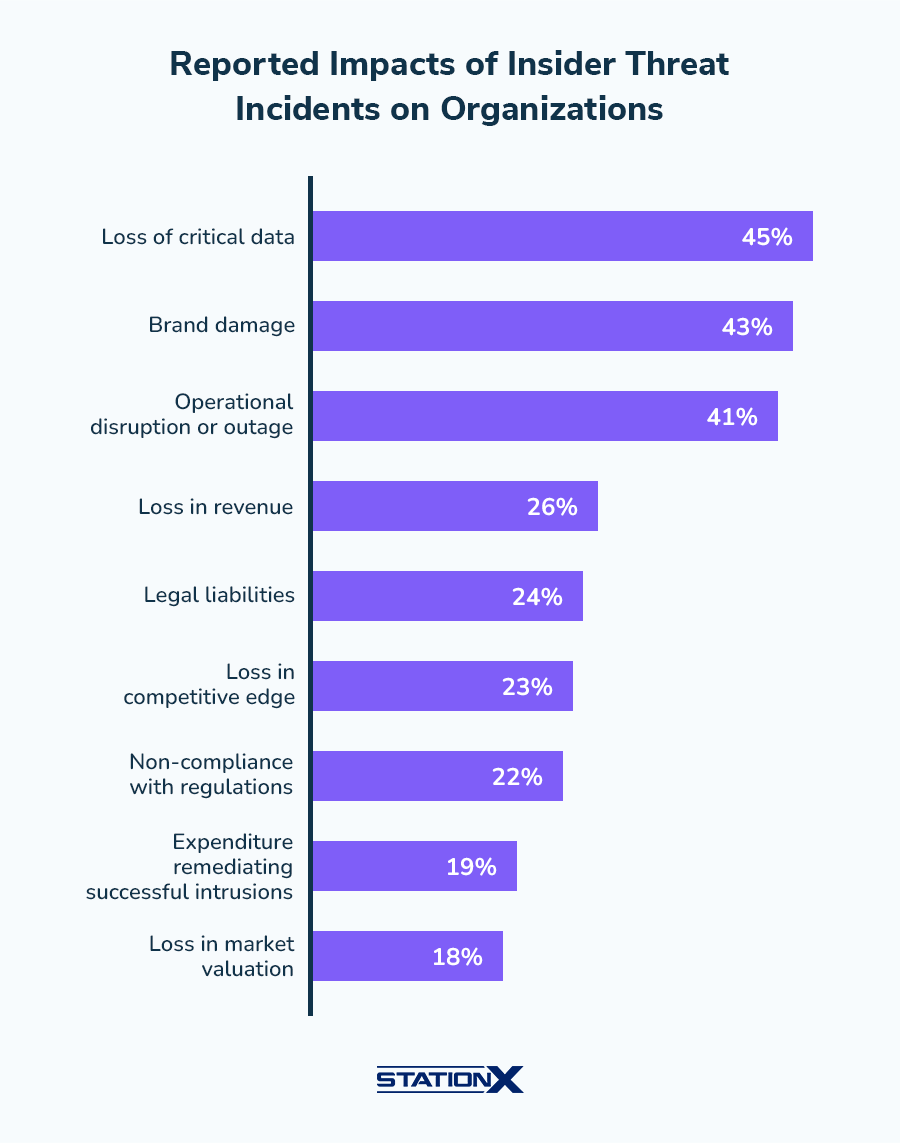
Insider threats create ripple effects throughout organizations. Financial data stands out as the most vulnerable asset, with 44% of organizations listing it as their top concern. The costs hit organizations differently based on their size. Large organizations with over 75,000 employees spend average costs of $24.60 million. Small organizations with fewer than 500 employees face costs around $8.00 million.
Common Attack Vectors
Malicious insiders often use these attack methods:
- Email transmission of sensitive data to outside parties (67% of cases)
- Unauthorized access to sensitive data outside their role (66% of cases)
- System vulnerability scanning (63% of cases)
Cloud services and IoT devices pose the biggest risks for insider-driven data loss. These channels account for 59% and 56% of incidents respectively. This pattern shows how modern workplace infrastructure creates new security challenges. Organizations struggle to maintain reliable security controls in distributed environments.
Implementing Least Privilege Access
Least privilege access is the life-blood of any insider threat prevention strategy. This approach substantially reduces an attack surface and streamlines processes. The principle of least privilege (PoLP) ensures users, services, and applications have exactly the access they need – nothing more, nothing less.
Core Principles of Least Privilege
Successful implementation of least privilege starts with understanding its fundamental principles. Users should only access specific data, resources, and applications needed to complete their required tasks. This strategy works especially when you have organizations that need protection from cyberattacks and the financial, data, and reputational losses that follow security incidents.
Role-Based Access Control Framework
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) serves as a main framework to enforce least privilege principles. RBAC offers a well-laid-out approach where administrators assign permissions to roles and then assign roles to users. Here’s a proven implementation approach:
- Define clear roles based on job functions
- Map specific permissions to each role
- Establish access review processes
- Implement automated policy enforcement
This framework has shown remarkable results by eliminating individual permission handling and streamlining access management.
Just-in-Time Access Management
Security posture improves after adopting Just-in-Time (JIT) access management. Users receive access to accounts and resources for a limited time when needed. JIT access substantially reduces risks associated with standing privileges where users have unlimited access to accounts and resources.
JIT access implementation has delivered impressive results. It improves organizational compliance and simplifies audits by logging privileged-access activities centrally. Teams maintain tight security without sacrificing operational productivity by controlling three critical elements—location, actions, and timing.
This all-encompassing approach to least privilege access creates reliable defense against insider threats. Teams retain the access they need to perform their duties effectively.
Technical Controls and Tools
An insider threat prevention strategy should include strong technical controls and advanced tools that work seamlessly with a least privilege framework. It’s necessary to complete defense against potential insider threats by combining sophisticated monitoring capabilities with automated management systems.
Access Management Solutions
Modern access management solutions such as Apono give us unprecedented visibility into user behavior and potential risks. This includes detecting and blocking suspicious activities immediately through advanced threat analytics, while privacy controls help maintain compliance and user trust. These solutions prevent data exfiltration through common channels such as USB devices, web uploads, and cloud synchronization. The endpoint controls adjust based on individual risk profiles.
Automated Access Review Tools
Automated access review tools have changed how companies manage user privileges. These solutions maintain security and reduce the time spent on typical reviews by up to 90%. The automation capabilities include:
- Pre-built integrations for consolidating account access data
- Continuous access monitoring for faster user de-provisioning
- Simplified reviewer workflows and remediation management
The automated tools use sophisticated algorithms and predefined rules to perform user access reviews with minimal human involvement. These tools work especially when you have large-scale operations.
Measuring Implementation Success
Building measurement systems that work is vital to prove an insider threat prevention strategy right. This detailed approach to measuring success helps show the program’s value and spots areas that can be improved.
Key Performance Indicators
The way to measure an insider threat program’s effectiveness depends on the organization’s specific needs and business goals. This KPI framework uses both operational and programmatic metrics to paint a complete picture, tracking:
- Number of insider threat cases opened and resolved
- Average incident resolution time
- Value of protected assets and data
- Risk mitigation actions implemented
Compliance Reporting
Reports are the foundations of any compliance strategy. It’s important to find a solution that creates detailed reports that track user access patterns, exceptions, and review outcomes. This structure helps to stay compliant with various regulatory frameworks including GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX.
Conclusion
A multi-layered approach needs least privilege access, strong technical controls, and detailed measurement systems to prevent insider threats. Companies can reduce their attack surface and still work efficiently when they use role-based frameworks and just-in-time management for least privilege access. Multiple layers of protection against potential insider threats emerge from advanced monitoring tools and automated access reviews that strengthen these defenses.
These strategies combine to build strong defenses against the growing insider threat challenge. Organizations can safeguard their sensitive data and systems while creating productive work environments by carefully putting these practices in place. The detailed approach helps cut down the huge financial cost of insider incidents, which now average $15.4 million annually.