Cloud Security Assessment: Checklist to Ensure Data Protection
The adoption of cloud computing has become a cornerstone of modern business operations today. However, this shift brings forth significant concerns about data protection and security.
Cloud security assessment plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Organizations must prioritize this process to identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and establish robust security measures within their cloud environments.
Rising Cloud Adoption Trends
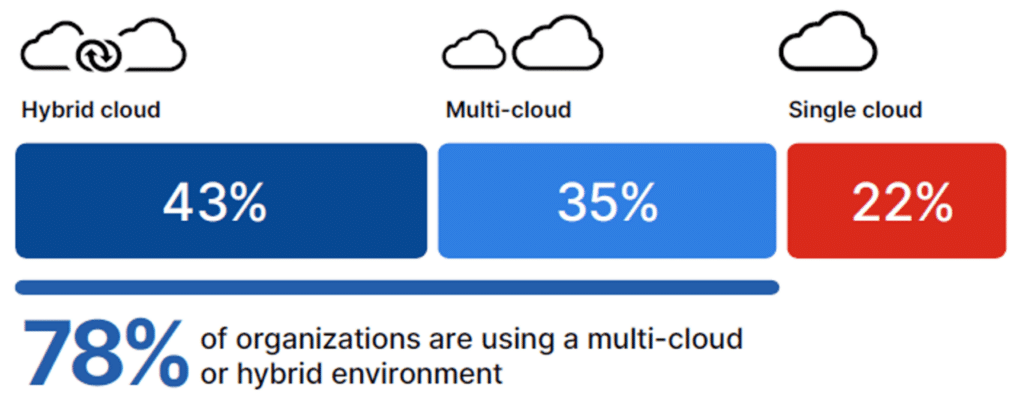
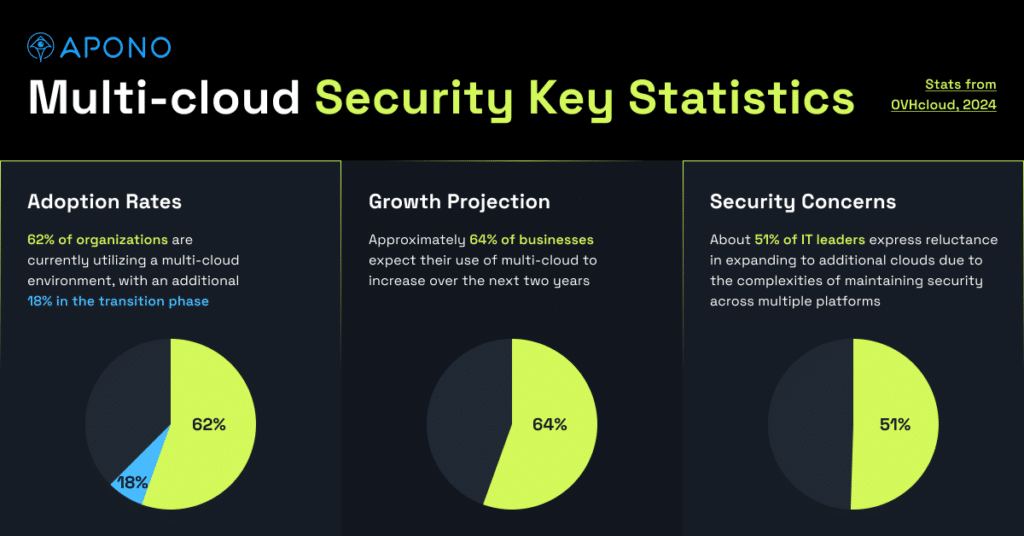
The shift towards cloud computing has been significant, with research indicating that 60% of the world’s corporate data is now stored in the cloud. As organizations embrace cloud solutions for their scalability and cost-effectiveness, they must also address the expanded attack surface and new security challenges that come with this transition.
Evolving Threat Landscape
The cloud security landscape is constantly evolving, presenting new challenges for organizations to navigate. Misconfiguration remains one of the leading causes of cloud breaches, as highlighted by the Thales 2024 Cloud Security Study. This issue is exacerbated by the fact that 88% of cloud data breaches are caused by human error. The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in cloud environments has introduced new vulnerabilities, such as model data poisoning and sophisticated phishing campaigns.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
As cloud adoption increases, so does the need for regulatory compliance. Organizations must adhere to various industry-specific regulations, such as HIPAA for healthcare, PCI DSS for credit card information, and GDPR for European Union citizen data. Cloud security assessments help ensure that organizations meet these compliance requirements and implement necessary administrative and technical controls to protect sensitive information.
To address these challenges, organizations are increasingly adopting zero-trust security models, with 87% now focusing on this approach. Cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools and cloud workload protection platforms (CWPP) have become essential for managing the dynamic nature of cloud environments and ensuring compliance objectives are met.
Regular cloud security assessments are vital for identifying vulnerabilities, mitigating risks, and maintaining a strong security posture. These evaluations help organizations detect misconfigurations, assess the effectiveness of existing security controls, and develop strategies to address potential threats. By conducting thorough assessments, businesses can reduce the risk of data breaches, improve their resilience against attacks, and demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive information in the cloud.
Key Steps in Cloud Security Assessment
A comprehensive cloud security assessment involves several crucial steps to ensure data protection and identify potential vulnerabilities. Organizations can strengthen their cloud security posture by following these key steps.
- Asset Inventory and Classification
The first step in a cloud security assessment is to conduct a thorough inventory of all cloud assets. This process involves identifying and categorizing all cloud-based resources, including virtual machines, storage volumes, network devices, APIs, and applications. By maintaining a complete list of assets, organizations gain visibility into their cloud infrastructure and can make informed decisions about maintenance, monetization, and security.
Asset classification is equally important. This involves categorizing cloud assets based on their criticality, purpose, and compliance requirements. By classifying assets according to their sensitivity, organizations can determine which assets are most at risk and need enhanced protection.
- Risk Identification and Analysis
Once the asset inventory is complete, the next step is to identify potential threats and analyze associated risks. This involves evaluating both external threats, such as hackers, and internal threats, like malicious insiders. Organizations should perform thorough testing of their cloud infrastructure to determine how easily external threat actors could access sensitive information.
Risk analysis involves considering the likelihood of a threat occurring and its potential impact on the business. By evaluating risks associated with each identified threat, organizations can prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- Security Control Evaluation
Assessing existing security controls is a critical component of a cloud security assessment. This step involves reviewing identity and access management policies, network security measures, data protection protocols, and incident response plans. Organizations should evaluate the effectiveness of their current security controls and identify any gaps or weaknesses that need to be addressed.
Key areas to focus on during security control evaluation include:
- Access control and authentication mechanisms
- Data encryption practices for data at rest and in transit
- Network segmentation and firewall configurations
- Monitoring and logging capabilities
- Compliance with industry regulations and standards
- Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing
The final key step in a cloud security assessment is to conduct vulnerability assessments and penetration testing. Vulnerability scanning tools can help identify potential weaknesses in cloud workloads and configurations. These tools continuously scan critical workloads and identify risks and misconfigurations, enabling organizations to address vulnerabilities proactively.
Penetration testing, often conducted by third-party experts, simulates real-world attacks to identify vulnerabilities that may not be apparent through automated scans. This process helps organizations stay one step ahead of potential attackers by uncovering both known and unknown security issues.
By following these key steps in cloud security assessment, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their cloud security posture, identify potential risks and vulnerabilities, and implement effective security measures to protect their valuable assets in the cloud.
Addressing Common Cloud Security Risks
Cloud security assessments play a crucial role in identifying and mitigating common risks associated with cloud environments. Organizations must be vigilant in addressing these vulnerabilities to ensure robust data protection and compliance.
Data breaches and unauthorized access remain significant concerns for businesses leveraging cloud services. According to a study by IBM, data breaches caused by cloud security vulnerabilities cost companies an average of USD 4.80 million to recover. This substantial expense includes the cost of investigating and repairing the breach, as well as potential fines or penalties imposed by regulators. To minimize this threat, organizations should implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) across their cloud infrastructure and enforce strong password policies.
Misconfiguration and inadequate change control pose another critical risk to cloud security. The National Security Agency (NSA) considers cloud misconfiguration a leading vulnerability in cloud environments. Shockingly, up to 99% of cloud environment failures are expected to be attributed to human errors by 2025. To address this issue, organizations should implement automated cloud monitoring solutions that leverage machine learning to detect misconfigurations in real-time. Additionally, establishing a robust change management process can help prevent unintended security gaps.
Insecure APIs and cloud service vulnerabilities are increasingly becoming targets for cybercriminals. As the use of APIs proliferates in modern software development, it’s crucial to implement proper security measures. Organizations should employ web application firewalls (WAFs) to filter requests by IP address or HTTP header information and detect code injection attacks. Implementing DDoS protection and regularly updating software and security configurations are also essential steps in securing APIs.
To effectively address these common cloud security risks, organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Conduct regular security assessments and vulnerability scans to identify potential weaknesses in cloud infrastructure.
- Implement the principle of least privilege for all cloud resources and users, ensuring that access is granted only on a need-to-know basis.
- Utilize cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to continuously monitor and assess the security state of cloud environments.
- Develop and enforce comprehensive security policies that address cloud-specific risks and compliance requirements.
- Provide ongoing security awareness training to employees, focusing on cloud security best practices and potential threats.
By addressing these common cloud security risks and implementing a robust security strategy, organizations can significantly enhance their cloud security posture and protect sensitive data from potential breaches and unauthorized access.
Implementing a Robust Cloud Security Strategy
Implementing a robust cloud security strategy is crucial for organizations to safeguard their digital assets and ensure data protection in the ever-evolving cloud landscape. A well-crafted approach helps businesses address potential vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Developing Security Policies and Procedures
To establish a strong foundation for cloud security, organizations must develop comprehensive security policies and procedures. These guidelines should outline rules for using cloud services safely, define data storage practices, and specify responsibilities for different aspects of cloud security. A cloud security policy serves as a critical document that provides clear instructions for users to access workloads securely and sets out ways to handle cloud security threats.
When creating a cloud security policy, it’s essential to identify the purpose and scope of the document. This includes specifying which cloud services, data types, and users are covered by the policy. Additionally, the policy should address key areas such as data classification, access control, encryption requirements, and incident response procedures.
Organizations should also consider implementing a cloud governance framework to ensure proper management of data security, system integration, and cloud computing deployment. This framework helps balance resource allocation and risk management while emphasizing accountability and continuous compliance with evolving regulations.
Employee Training and Awareness
One of the most critical steps in implementing a robust cloud security strategy is investing in employee training and awareness programs. These initiatives help staff understand the risks associated with cloud computing and how to prevent security breaches. By educating employees on security best practices and conducting regular training sessions, businesses can better protect their data and minimize the risk of security incidents.
Effective employee training programs should cover various topics, including:
- Recognizing and responding to potential threats
- Setting strong passwords and managing access credentials
- Identifying social engineering attacks
- Understanding risk management principles
- Emphasizing the risks of shadow IT and unauthorized tool usage
Regular discussions and specialized training for security personnel can further enhance the organization’s overall security posture and promote a culture of security awareness.
Incident Response and Disaster Recovery Planning
A crucial component of a robust cloud security strategy is the development of incident response and disaster recovery plans. These plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach or system failure, ensuring that organizations can quickly and effectively respond to threats and minimize potential damage.
Key elements of an effective incident response plan include:
- Clearly defined roles and responsibilities for team members
- Procedures for detecting and assessing security incidents
- Steps for containing and mitigating the impact of incidents
- Communication protocols for internal and external stakeholders
- Processes for collecting and preserving evidence for forensic analysis
Organizations should regularly test and update their incident response plans to ensure their effectiveness in addressing evolving threats and changing cloud environments. This may involve conducting simulated exercises or active scenarios to identify potential gaps and make necessary adjustments.
In addition to incident response planning, organizations should also develop comprehensive disaster recovery strategies. These plans should address various scenarios, including data loss, system failures, and natural disasters. By implementing robust backup and recovery processes, businesses can ensure the continuity of their operations and minimize downtime in the event of a catastrophic incident.
By focusing on these key areas – developing security policies, providing employee training, and implementing incident response and disaster recovery plans – organizations can create a strong foundation for their cloud security strategy. This approach helps protect sensitive data, maintain compliance with regulations, and ensure the resilience of cloud-based systems in the face of evolving threats.
Conclusion
Cloud security assessment has a significant impact on ensuring data protection in today’s digital landscape. As organizations continue to adopt cloud technologies, the need to address security concerns and comply with regulations becomes increasingly crucial. By following key steps such as asset inventory, risk analysis, and vulnerability testing, businesses can strengthen their cloud security posture and safeguard sensitive information.
To wrap up, implementing a robust cloud security strategy involves developing comprehensive policies, providing employee training, and creating incident response plans. These measures help organizations to minimize risks, maintain compliance, and respond effectively to potential threats. As the cloud environment continues to evolve, regular assessments and updates to security practices are essential to protect valuable assets and maintain trust in cloud-based operations.
How Apono Helps
Apono is a cloud security and access management tool that focuses on providing secure and efficient access to sensitive resources in cloud environments. It plays a significant role in cloud security assessments by automating and enhancing the security posture of cloud infrastructure. Here are some key ways Apono assists with cloud security assessments:
1. Automated Access Controls:
– Just-in-Time (JIT) Access: Apono enables JIT access to cloud resources, allowing users to request temporary access for a specified time. This reduces the attack surface by ensuring that sensitive resources are not persistently exposed.
– Granular Permissions: It ensures that users have only the minimum necessary permissions by enforcing the principle of least privilege, which is essential for reducing risks in cloud security.
– Role-based Access Control (RBAC): Apono helps implement RBAC models, ensuring that permissions are assigned based on roles, which makes it easier to manage and audit access.
2. Real-time Monitoring and Auditing:
– Continuous Monitoring: Apono provides real-time monitoring of access events, making it easier to track who accessed what resources and when. This is critical for identifying unauthorized or risky activities during security assessments.
– Audit Logs: It offers comprehensive logging and auditing features, giving security teams visibility into access patterns. These logs are vital for post-incident investigations and compliance with regulatory requirements.
3. Policy Enforcement:
– Access Policies: Apono enforces custom access policies that align with an organization’s security requirements, ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive cloud resources.
– Compliance Automation: It helps automate compliance checks by ensuring access policies are in line with industry standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2), which is crucial during cloud security assessments.
4. Cloud Environment Integration:
– Multi-Cloud Support: Apono integrates with various cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP), making it easier to manage access across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. This provides a unified approach to access management, simplifying cloud security assessments across different platforms.
– Identity Providers (IdP) Integration: It integrates with existing identity providers like Okta or Active Directory, ensuring that identity and access management (IAM) policies are consistently applied.
5. Threat Detection and Response:
– Anomalous Access Detection: Apono helps identify anomalous access behavior that could indicate potential security breaches or insider threats. It can alert security teams when unusual patterns are detected during assessments.
– Automated Remediation: In case of a detected threat or policy violation, Apono can trigger automated remediation processes, such as revoking access or adjusting permissions in real time.
6. Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM):
– Continuous Compliance: Apono assists in cloud security assessments by ensuring continuous compliance with cloud security best practices. It highlights misconfigurations, excessive privileges, and other vulnerabilities that could compromise cloud infrastructure security.
By automating access control, monitoring user behavior, enforcing policies, and providing audit trails, Apono strengthens an organization’s cloud security strategy and simplifies cloud security assessments. This helps security teams ensure that sensitive cloud resources are protected against unauthorized access and other potential risks.