With an average of more than 5 data breaches globally a day, it’s clear companies need a way to prevent data loss. This is where a data loss prevention policy comes into play.
A data loss prevention policy serves as a crucial safeguard against unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations. This comprehensive framework outlines strategies and procedures to identify, monitor, and protect valuable data assets across an organization’s network, endpoints, and cloud environments.
Why is it important?
Data loss is a critical issue with significant implications for businesses and individuals. Here are some important statistics related to data loss in cybersecurity:
1. Data Breach Frequency
2. Human Error and Cybersecurity
3. Cost of Data Loss
4. Ransomware and Data Loss
- In 2023, 40% of organizations that experienced a ransomware attack also reported data loss, either due to non-payment or incomplete recovery after decryption.
- Source: Sophos 2023 State of Ransomware Report.
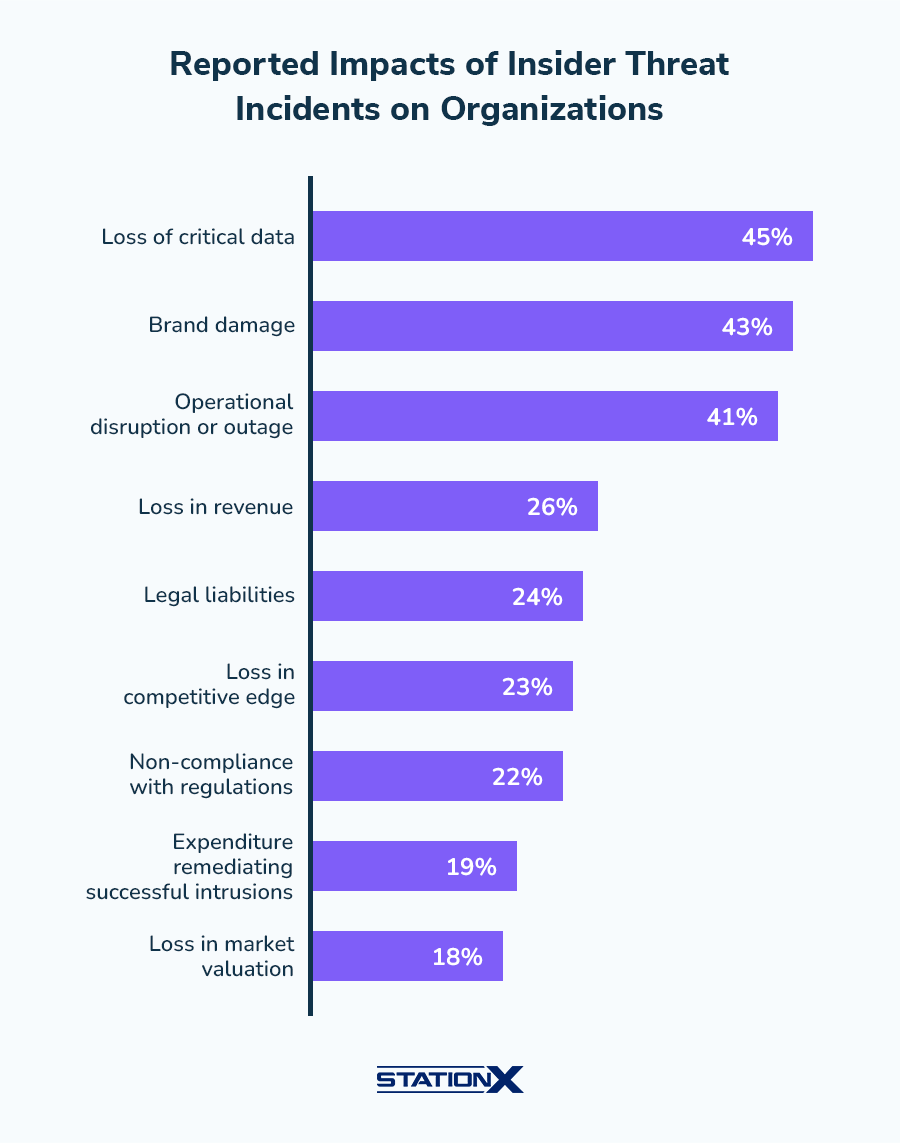
5. Insider Threats
6. Phishing and Credential Theft
7. Cloud Data Risks
- Nearly 45% of organizations experienced data loss incidents in the cloud due to misconfigurations, inadequate security controls, and excessive access permissions.
- Source: Thales Cloud Security Report 2023.
8. Time to Detect and Contain Breaches
- The average time to identify and contain a data breach was 277 days in 2023. Breaches involving sensitive data typically took longer to detect and mitigate, resulting in more significant losses.
- Source: IBM Security 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report.
9. Remote Work and Data Loss
- Organizations with remote or hybrid work arrangements saw an increase in data loss incidents, with 45% of companies reporting difficulties securing sensitive data in remote work environments.
- Source: Code42 2023 Data Exposure Report.
10. Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Gaps
- Despite the growing investment in DLP technologies, 68% of organizations report experiencing data loss incidents due to inadequate or misconfigured DLP systems.
- Source: Forrester DLP Research 2023.
These statistics demonstrate that data loss in cybersecurity is driven by a combination of human errors, external attacks, and inadequate security measures, making comprehensive strategies essential for prevention.
Creating a Data Loss Prevention Policy
Creating an effective data loss prevention policy involves several key steps. Organizations need to assess their data landscape, develop a robust strategy, implement the right tools, and engage employees in the process. By following best practices and adopting proven methods, companies can strengthen their data security posture, meet regulatory requirements, and safeguard their most valuable information assets. This guide will walk through the essential steps to create a strong data loss prevention policy tailored to your organization’s needs.
Analyze Your Organization’s Data Landscape
To create an effective data loss prevention policy, organizations must first gain a comprehensive understanding of their data landscape. This involves identifying various data types, mapping data flows, and assessing current security measures. By thoroughly analyzing these aspects, companies can lay a solid foundation for their data loss prevention strategy.
Identify Data Types and Sources
The initial step in developing a robust data loss prevention policy is to identify and categorize the different types of data within the organization. This process involves a detailed examination of various data categories, including personal customer information, financial records, intellectual property, and other sensitive data that the organization handles.
Organizations should classify data based on its sensitivity and relevance to business operations. For instance, personal customer information such as names, addresses, and credit card details should be categorized as highly sensitive, requiring enhanced protective measures. In contrast, data like marketing metrics might be classified as less sensitive and safeguarded with comparatively less stringent security protocols.
It’s crucial to examine all potential data sources, such as customer databases, document management systems, and other repositories where data might reside. This comprehensive approach helps ensure that no sensitive information is overlooked in the data loss prevention strategy.
Map Data Flow and Storage
Once data types and sources have been identified, the next step is to map how data flows within the organization. This process involves tracing the journey of data from the point of collection to storage, processing, and sharing. Understanding these data flows is essential for identifying potential vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate security measures.
Organizations should pay special attention to different types of data, including personally identifiable information (PII), payment details, health records, and any other sensitive information handled by the organization. It’s important to consider how each data type is used and shared within and outside the organization, as well as the purposes for which various data types are collected and processed.
When mapping data flows, organizations should focus particularly on identifying flows that involve sensitive information. Evaluating the level of risk associated with these flows, especially those that include third-party vendor interactions or cross-border data transfers, is crucial as such flows often present higher risks compared to data used solely within the organization.
Assess Current Security Measures
The final step in analyzing the organization’s data landscape is to evaluate existing security measures. This assessment helps identify gaps in current protection strategies and provides insights for improving the overall data loss prevention policy.
Organizations should implement monitoring and auditing mechanisms to track access to sensitive data and detect suspicious or unauthorized activities. This includes monitoring user activity logs, access attempts, and data transfers to identify potential security incidents or breaches. Regular security audits and assessments should be conducted to ensure compliance with security policies and regulations.
It’s also important to review and update security policies, procedures, and controls regularly to adapt to evolving threats and regulatory requirements. Ensure that security policies are comprehensive, clearly communicated to employees, and enforced consistently across the organization. By regularly assessing and improving security measures based on emerging threats, industry best practices, and lessons learned from security incidents, organizations can strengthen their data loss prevention policy and better protect sensitive information.
Create a Comprehensive DLP Strategy
Creating a robust data loss prevention policy involves several key steps to ensure the protection of sensitive information. Organizations need to define clear objectives, establish a data classification schema, and develop incident response plans to effectively safeguard their data assets.
Define Policy Objectives
To create an effective data loss prevention policy, organizations must first define clear objectives. These objectives should align with the company’s overall security strategy and regulatory requirements. The primary goal of a DLP policy is to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and compliance violations.
Organizations should identify the types of sensitive data they handle, such as personally identifiable information (PII), financial records, and intellectual property. By understanding the nature of their data landscape, companies can tailor their DLP objectives to address specific risks and vulnerabilities.
When defining policy objectives, it’s crucial to consider regulatory compliance requirements. Many industries are subject to data protection regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Ensuring compliance with these standards should be a key objective of any comprehensive DLP strategy.
Establish Data Classification Schema
A critical component of a strong data loss prevention policy is the implementation of a data classification schema. This framework helps organizations categorize their data based on sensitivity levels, enabling them to apply appropriate security measures to different types of information.
A typical data classification schema might include categories such as public, internal, confidential, and highly sensitive. Each category should have clear criteria and guidelines for handling and protecting the data within it. For instance, highly sensitive data might require encryption and strict access controls, while public data may have fewer restrictions.
To establish an effective data classification schema, organizations should:
- Identify and inventory all data types within the company
- Define classification levels based on data sensitivity and business impact
- Develop criteria for assigning data to each classification level
- Implement processes for labeling and tagging data according to its classification
- Train employees on the data classification system and their responsibilities
By implementing a robust data classification schema, organizations can ensure that appropriate security measures are applied to different types of data, reducing the risk of data loss and unauthorized access.
Develop Incident Response Plans
An essential aspect of a comprehensive data loss prevention policy is the development of incident response plans. These plans outline the steps to be taken in the event of a data breach or security incident, helping organizations minimize damage and recover quickly.
Incident response plans should include:
- Clear definitions of what constitutes a security incident
- Roles and responsibilities of team members involved in incident response
- Step-by-step procedures for containing and mitigating the impact of a breach
- Communication protocols for notifying stakeholders and authorities
- Procedures for documenting and analyzing incidents to prevent future occurrences
Organizations should regularly review and update their incident response plans to ensure they remain effective in the face of evolving threats and changing business environments. Conducting mock drills and simulations can help test the effectiveness of these plans and identify areas for improvement.
Select and Implement DLP Tools
Selecting and implementing the right data loss prevention tools is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring regulatory compliance. Organizations should carefully evaluate DLP solutions, deploy data discovery and classification tools, and configure policy enforcement mechanisms to create a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Evaluate DLP Solutions
When evaluating DLP solutions, organizations should consider their specific needs and regulatory requirements. It’s essential to choose vendors that can protect data across multiple use cases identified during the data flow mapping activity. Many organizations implement DLP to comply with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, as well as to protect intellectual property.
To select the most appropriate DLP tool, consider the following factors:
- Coverage: Ensure the solution provides protection across various data environments, including endpoints, networks, and cloud applications.
- Data discovery capabilities: Look for tools that can efficiently scan local, network, and cloud repositories to identify sensitive data.
- Policy templates: Choose a solution that offers pre-configured templates for common types of sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI).
- Customization options: The tool should allow for policy customization to address unique data handling requirements and adapt to new regulatory standards.
- Integration: Consider how well the DLP solution integrates with existing IT infrastructure to ensure seamless operation.
Deploy Data Discovery and Classification Tools
Implementing data discovery and classification tools is a critical step in the DLP process. These tools help organizations identify and categorize sensitive information across various storage locations, including file shares, cloud storage, and databases.
Key features to look for in data discovery and classification tools include:
- Automated scanning: The ability to automatically scan and classify data based on predefined criteria.
- Content-based classification: Tools that can analyze the content of files and documents to identify sensitive information.
- User-driven classification: Options for users to classify data during creation or modification.
- Continuous monitoring: Real-time scanning capabilities to detect and classify new or modified data.
- OCR detection: The ability to identify sensitive information in scanned documents and images.
Configure Policy Enforcement Mechanisms
Once DLP tools are selected and deployed, organizations must configure policy enforcement mechanisms to protect sensitive data effectively. This involves setting up rules and actions to be taken when potential violations are detected.
Consider the following when configuring policy enforcement:
- Granular controls: Implement flexible and fine-grained controls for enforcing data handling policies.
- Notification systems: Set up alerts and notifications for administrators and users when policy violations occur.
- Encryption: Configure automatic encryption for sensitive data before transmission or storage.
- Blocking mechanisms: Implement controls to block unauthorized actions on sensitive data, such as file transfers or sharing.
- User awareness: Configure policy tips and notifications to educate users about data protection policies and promote security consciousness.
By carefully selecting and implementing DLP tools, organizations can significantly enhance their data protection capabilities and reduce the risk of data loss or unauthorized access. Regular evaluation and improvement of these tools and policies are essential to maintain an effective data loss prevention strategy in the face of evolving threats and regulatory requirements.
Educate and Engage Employees
Educating and engaging is a crucial aspect of implementing an effective data loss prevention policy. By fostering a culture of security awareness, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conduct DLP Awareness Training
To create a robust data loss prevention strategy, organizations should implement comprehensive awareness training programs. These programs equip employees with the necessary skills to handle sensitive information responsibly. Using real-world examples of data breaches and their consequences can enhance the impact of these sessions, driving home the importance of following DLP protocols.
Organizations should consider implementing role-based training programs that cater to the specific data access needs of different departments. For instance, marketing teams may require training on handling customer databases and complying with data protection laws, while IT staff might need more in-depth training on data security and relevant legislation.
To make training more effective, organizations can use various approaches, such as:
• Interactive exercises and role-play scenarios to simulate data privacy situations
• Just-in-time training solutions for specific tasks
• Organizing privacy policy hackathons to find potential improvements
• Starting a data protection debate club to explore different viewpoints
Implement User Behavior Analytics
User Entity and Behavior Analytics (UEBA) is an advanced cybersecurity technology that focuses on analyzing the behavior of users and entities within an organization’s IT environment. By leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, UEBA can detect anomalies in user behavior and unexpected activities occurring on network devices.
UEBA helps organizations identify suspicious behavior and strengthens data loss prevention efforts. It can detect various threats, including:
• Malicious insiders with authorized access attempting to stage cyberattacks
• Compromised insiders using stolen credentials
• Data exfiltration attempts through unusual download and data access patterns
By implementing UEBA, organizations can enhance their ability to detect and prevent cyber threats effectively, providing real-time monitoring and early threat detection.
Establish Clear Communication Channels
To ensure the success of a data loss prevention policy, organizations must establish clear communication channels for disseminating information and addressing concerns. This can be achieved through:
• Regular organization-wide communications, such as newsletters or bite-sized lunchtime training sessions covering hot topics
• Utilizing internal systems like intranets to communicate with engaged staff members
• Sending out weekly privacy tips via email or internal messaging systems
• Creating an internal knowledge base that serves as a central repository for DLP best practices, policies, and FAQs
By implementing these strategies, organizations can create a comprehensive data loss prevention policy that engages employees and integrates with existing systems, ultimately safeguarding sensitive data and promoting a security-conscious culture throughout the organization.
Conclusion
Creating a robust data loss prevention policy is a crucial step to safeguard sensitive information and meet regulatory requirements. By following the steps outlined in this guide, organizations can develop a comprehensive strategy that protects data across various environments. This approach includes analyzing the data landscape, creating a tailored DLP strategy, implementing the right tools, and engaging employees in the process.
The success of a DLP policy hinges on continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving threats. Regular assessments, updates to security measures, and ongoing employee training are key to maintaining an effective data protection strategy. By making data loss prevention a priority, organizations can minimize risks, build trust with stakeholders, and ensure the long-term security of their valuable information assets.
How Apono Assists
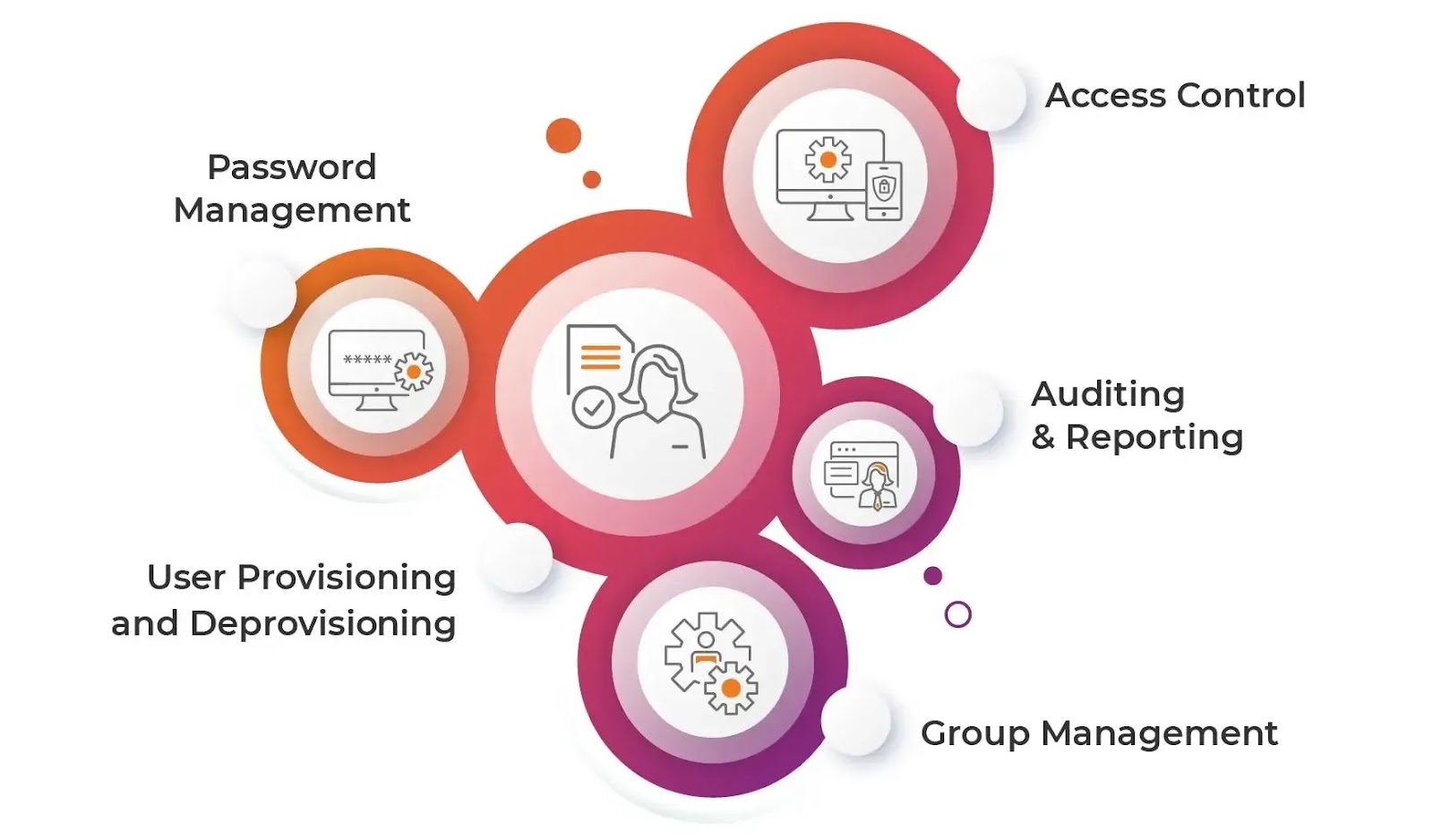
Apono helps with creating a Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policy by simplifying access management and enforcing security best practices. Here’s how Apono contributes to an effective DLP:
1. Granular Access Control
Apono allows for fine-tuning of user permissions, granting access only to specific data and resources needed for a particular role. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized data exposure, which is crucial for DLP.
2. Automated Access Governance
Apono automates the process of granting, revoking, and reviewing permissions. This means you can set up policies that limit data access based on role, project, or even time, reducing the chance of sensitive data leakage.
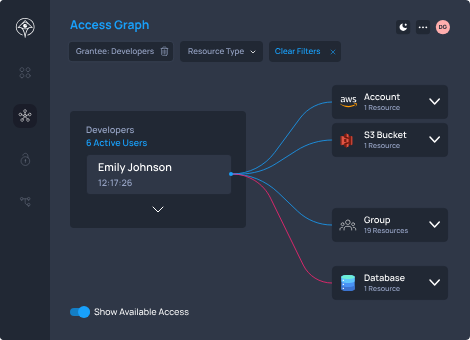
3. Real-time Monitoring and Auditing
Apono provides real-time monitoring of access events, allowing you to track who accessed what and when. This visibility helps in detecting potential data breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
4. Policy Enforcement Through Workflows
With Apono, you can create workflows that enforce specific policies, like requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing sensitive data or automatically removing access after a project ends. These policies reduce the risk of data loss by ensuring that only verified and authorized users can access critical information.
5. Least Privilege and Just-in-Time Access
Apono promotes the principle of least privilege by allowing users to request temporary access to data when needed. Just-in-time access reduces the window of exposure for sensitive data, helping to prevent accidental or malicious data loss.
6. Integration with Existing Security Tools
Apono integrates with various identity providers (like Okta or Azure AD) and cloud platforms, allowing you to enforce consistent DLP policies across your tech stack. It ensures that data loss prevention is maintained across the organization’s entire infrastructure.
By using Apono for access control, companies can establish a comprehensive DLP policy that safeguards sensitive data through automated governance, access restrictions, and monitoring.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policy Template
Purpose
The purpose of this Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Policy is to protect sensitive and confidential information from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction. The policy outlines the measures to prevent, detect, and respond to potential data loss and ensure compliance with applicable regulations.
Scope
This policy applies to all employees, contractors, consultants, and third-party users who have access to the organization’s systems, networks, and data. It covers all forms of data including but not limited to electronic, physical, and cloud-based data storage.
1. Policy Statement
The organization is committed to safeguarding sensitive data, including Personally Identifiable Information (PII), financial data, intellectual property, and proprietary information. All employees are responsible for complying with the DLP measures outlined in this policy.
2. Roles and Responsibilities
- Data Owners: Responsible for identifying and classifying data according to its sensitivity.
- IT Department: Responsible for implementing and managing DLP technologies and processes.
- Security Team: Responsible for monitoring data flow, detecting potential incidents, and responding accordingly.
- All Employees: Responsible for adhering to DLP policies, reporting suspected data loss, and following security best practices.
3. Data Classification
All organizational data should be classified according to its sensitivity:
- Public: Information that can be freely shared without risk.
- Internal: Non-sensitive information intended for internal use.
- Confidential: Sensitive information that could cause harm if exposed.
- Restricted: Highly sensitive information with strict access controls.
4. Data Handling Procedures
4.1 Data Access Control
- Access to sensitive data is granted based on the principle of least privilege.
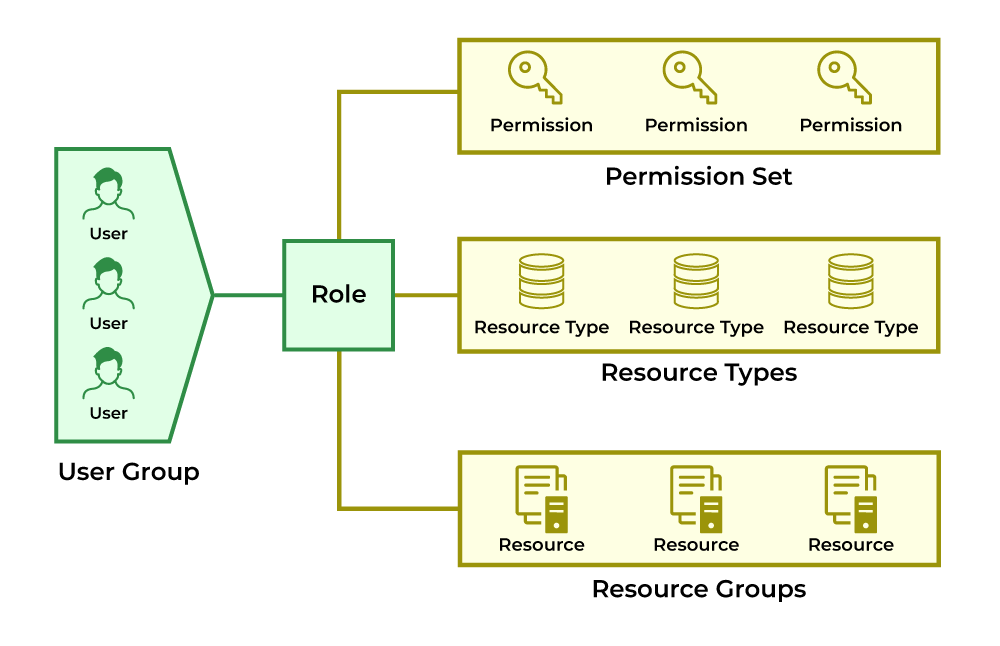
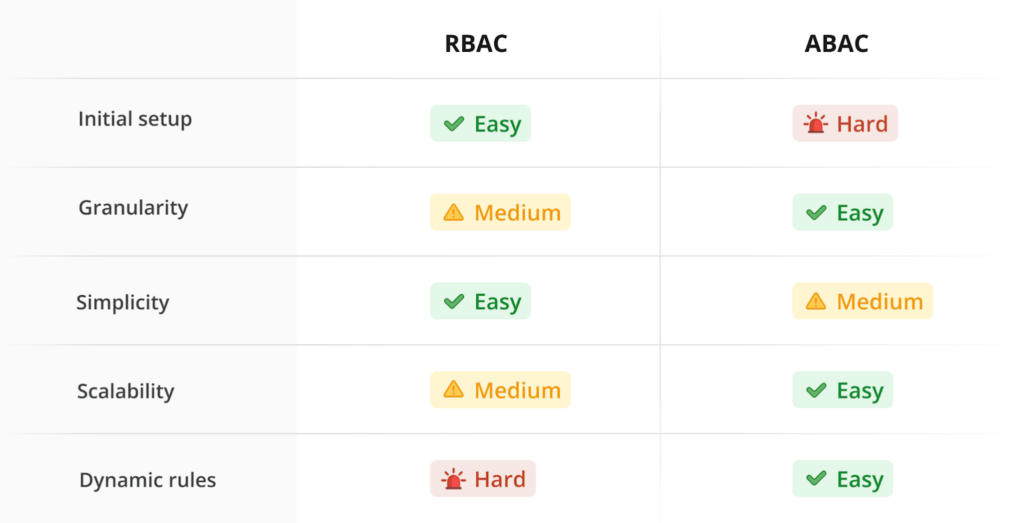
- Role-based access control (RBAC) should be implemented to ensure only authorized personnel access sensitive data.
4.2 Data Encryption
- Data must be encrypted both at rest and in transit using industry-standard encryption protocols.
- All portable devices (laptops, USB drives, etc.) must have encryption enabled.
4.3 Data Transmission
- Sensitive data transmitted over the network must use secure transmission protocols (e.g., SSL/TLS).
- Employees must not use personal email accounts or unsecured channels to send sensitive data.
4.4 Data Storage
- Sensitive data must be stored only on approved and secure locations (e.g., secure servers, encrypted drives).
- Data stored in cloud services must follow the organization’s cloud security policy.
5. DLP Technology and Tools
The organization will implement Data Loss Prevention technologies to monitor, detect, and block potential data leaks. These tools will:
- Monitor data transfer activities (email, USB transfers, file uploads).
- Detect unauthorized attempts to access or transfer sensitive data.
- Generate alerts for suspicious activities or policy violations.
6. Incident Response
In the event of a data loss or potential breach:
- Detection: The security team will investigate and confirm the incident.
- Containment: Immediate steps will be taken to stop further data loss.
- Notification: Relevant stakeholders, including legal and compliance teams, will be notified.
- Recovery: Affected systems will be restored, and data integrity will be verified.
- Post-Incident Review: The incident will be reviewed, and policies will be updated as necessary.
7. Employee Training
All employees must receive regular training on DLP policies and procedures, including:
- Recognizing phishing attempts and social engineering attacks.
- Proper data handling and sharing practices.
- The importance of reporting suspicious activities.
8. Compliance
The organization must comply with all applicable laws and regulations concerning data protection, including but not limited to:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) (if applicable)
- Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) (if applicable)
9. Policy Violations
Failure to comply with this DLP policy may result in disciplinary actions, including termination of employment, legal action, or other penalties as deemed appropriate.
10. Policy Review and Updates
This policy will be reviewed annually or when significant changes occur to the organization’s data management practices. Updates will be communicated to all employees.
Approval
This policy is approved by the organization’s management and is effective as of [Effective Date].
Signatures
Chief Information Officer
Data Protection Officer
This template can be customized according to specific organizational needs and industry regulations.